Recently, the National Rubber Tire Quality Supervision and Inspection Center released an analysis titled "Analysis of Common Passenger Car Tire Damage Caused by Improper Use."According to the center's statistics, over 80% of the disputes related to failures in passenger car radial tires in recent years are caused by improper use. The center has compiled and organized the ten most common problems and created a promotional sheet.
1. Impact with Foreign Objects Causing Ply Wire Breakage → Shoulder and Sidewall Bulging
Cause
While driving, the tire's shoulder or sidewall near the shoulder area strikes a foreign object (such as a pothole, curb, etc.). During the impact, the tire is compressed by the rim, causing the ply wires inside the tire to break. Under internal tire pressure, a bulge forms at the break or along the radial line of the break, leading to dents or cracks in the tire’s airtight layer.

Identification Features
Feature 1:

A black rubber imprint left on the rim edge at the location of the bulge after the tire strikes the foreign object.
Feature 2:

Damage marks near the tire bead area directly below the bulge caused by the tire being squeezed between the foreign object and the rim edge.
Feature 3:

Dents in the airtight rubber layer inside the tire (caused by the breakage of the ply wires near the tire shoulder). In severe cases, the airtight rubber layer may rupture.
2. Chronic Air Loss Leading to Under-inflation and Crushing Damage
Cause
When the tire operates at pressures lower than the recommended level or is underinflated, the tire body flexes excessively. The tire, rim, and ground create a contact surface, leading to circumferential breaks and damage in the airtight rubber layer and the ply fabric layer. Rubber particles and other debris may attach to the inside of the tire. In severe cases, the tire may split into two or three pieces.

Identification Features
Feature 1:
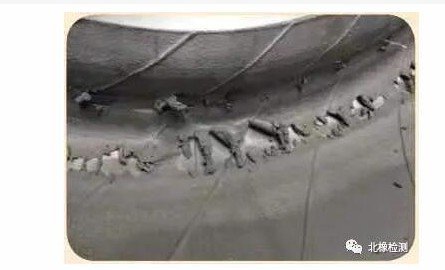
The airtight rubber layer inside the tire shows signs of scorching, with delamination between the rubber and ply fabric, and the ends of the ply wires become loose. This is caused by prolonged use of the tire in an underinflated state, causing excessive flexing and generating high heat.
Feature 2:

Circumferential creases in the airtight rubber layer (as shown in Photo 1) and circumferential friction marks on the outer side of the tire sidewall (as shown in Photo 2). These are caused by continued use of the tire under low pressure, leading to sidewall friction with the ground.

3. Tread Crown Impact Damage
Cause
The tread crown is impacted by a foreign object.
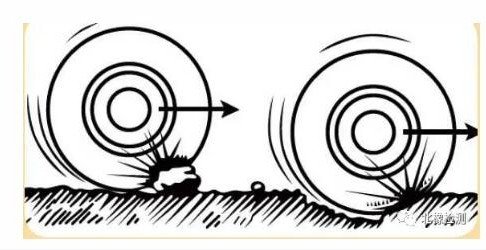
Identification Features
(1)Localized damage.
(2)The rubber at the damaged area is tightly bonded with the belt layer, and the belt layer’s ends show no loosening, indicating that there was no delamination prior to the damage.

4. Sidewall Impact Damage
Cause
The tire sidewall is impacted or scratched by a foreign object.
Identification Features
(1)Localized damage.
(2)The rubber at the damaged area is tightly bonded with the ply fabric material, and the ends of the ply wires show no loosening (as shown in Photo 1 and Photo 2), indicating that there was no delamination prior to the damage.

5. Sidewall Cut Damage
Cause
The tire sidewall is cut by a sharp foreign object.
Identification Features
(1)Localized damage.
(2)The rubber at the damaged area is tightly bonded with the ply fabric, and the ply wire ends show no loosening, indicating that there was no delamination prior to the damage.

6. Shoulder Cut Damage
Cause
The tire shoulder is cut by a sharp foreign object.
Identification Features
(1)Localized damage.
(2)The rubber at the damaged area is tightly bonded with the ply fabric, and the ply wire ends show no loosening, indicating that there was no delamination prior to the damage.

7. Irregular Wear -Camber Wear (One-Sided Wear)
Cause
The wheel’s camber angle (either positive or negative) exceeds the wheel alignment specifications allowed by the vehicle manufacturer.
Feature:
One side of the tire shoulder wears down more quickly than the other.
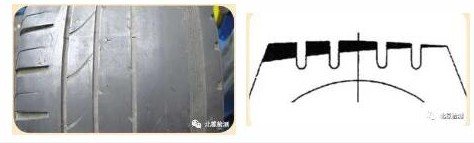
8. Irregular Wear-Feathering Wear
Cause
The wheel’s camber angle exceeds the wheel alignment specifications allowed by the vehicle manufacturer.
Identification Features
The edges of the tread blocks exhibit abnormal feathering wear.

9. Irregular Wear-Aggressive Driving
Cause
The tire undergoes high-speed steering, resulting in tread blocks being sheared off, or the tire sidewall frictioning laterally against the ground.
Identification Features
The tread exhibits a tearing pattern from one side to the other, with rubber peeling or shedding. The area under stress shows severe damage, while the extended areas show light wear.

10. Sidewall Puncture Leading to Slow Air Loss
Cause
The tire is punctured by a small but sharp foreign object (as indicated by the red circle).
Identification Features
A puncture of the size of a needle hole causes a gradual decrease in the tire's internal air pressure.